Generative AI based medical assistant on AWS

Yet another LLM-based chatbot
Generative AI and large language models (LLMs) are becoming increasingly popular, and small and big tech companies are releasing new solutions like ChatGPT, Bard, and Llama on a weekly basis. Corporations are looking for ways to use this technology to create company-wide knowledge sources and AI assistants to improve employee productivity, efficiency and access to internal knowledge.
In order to meet this demand, we decided at Smile to experiment with a lot of different tools already (read about it here and here) but we wanted to give it a try to the freshly available Amazon Bedrock service on AWS. We wanted to see whether it was easy to create generative AI based chatbots on AWS, and what could be the benefits of using it.
To experiment with this technology, we decided to create a Medical Assistant Chatbot, using Anthropic’s Claude v2 model hosted on AWS Bedrock service. The Claude family of large language models is purpose built for conversations, summarization, Q&A, workflow automation and coding, supporting multiple languages (we tried in English and French).
The Medical Assistant Chatbot can be used by patients to summarize, understand, and obtain more information about medical diagnostics.
For the need of this demo, users start by selecting a data preset containing a radiography image and diagnostic. Real life end-users would have to upload their record or connect to a third party service hosting that information. The chatbot then generates a response in the user’s preferred language.
Users can ask the chatbot to summarize or simplify the diagnostic or to provide more explanations and clarification with follow-up questions. Since we used the AI-generated diagnostics from radiography imaging, from research conducted by BIR (The British Institute of Radiology), radiography images are not used in the response generation. We just wanted to interpret results from medical staff, not run the diagnostic ourselves. Moreover, patients can also ask the chatbot to translate the diagnostic into another language.
Disclaimer: the objective of the demonstration is to provide explanations to non-medical persons and by no means to replace any medical staff.
AWS Bedrock
Now let’s have a deeper look at AWS’s new service called Bedrock. Bedrock is a new service that makes it easy for developers to build applications using generative AI. Developers can now focus on building their application without worrying about the underlying infrastructure of running and maintaining these models. It provides access to a variety of pre-built foundation models (FMs) from leading providers, including Amazon, Anthropic, Stable AI, and AI21 Labs.
Here are some of the benefits of using AWS Bedrock:
- Extensive access to a diverse array of FMs: AWS Bedrock provides an extensive selection of FMs designed for various tasks, including text summarization, image generation, and code generation. This empowers customers to choose the most suitable model that caters to their specific requirements.
- User-friendly: AWS Bedrock offers a straightforward API and a serverless experience that simplifies the initiation of generative AI endeavors. Developers can effortlessly engage with Bedrock through the utilization of the SDK or AWS CLI. Customers are relieved from the burden of managing infrastructure or possessing prior machine learning expertise.
- Highly scalable: AWS Bedrock possesses the capability to scale in order to accommodate the demands of even the most resource-intensive applications. Customers can effortlessly add or remove FMs as necessary, without the need to concern themselves with infrastructure management.
- Ensured security: Built upon AWS’s secure infrastructure, AWS Bedrock incorporates a diverse range of security features, including encryption and access control. These measures empower customers to safeguard their data and applications effectively.
AWS has recently made an announcement regarding the general availability of Bedrock in two AWS regions, namely N. Virginia and Oregon. It is worth mentioning that Bedrock will soon be accessible in other regions as well. Additionally, it is anticipated that Meta’s Llama 2 model will soon be made accessible on the Bedrock platform, along with the introduction of numerous other features.
The user interface of Bedrock is designed to be user-friendly and uncomplicated. It encompasses a dedicated playground area that facilitates the examination of inputs and corresponding outputs produced by various models, while also allowing for the fine-tuning of responses. This entails the ability to modify parameters such as top_k (enabling the sampling of the most probable subsequent tokens) and temperature (providing control over the level of randomness or uncertainty in the model’s prediction), thereby facilitating the evaluation of different prompts.
Technical Architecture
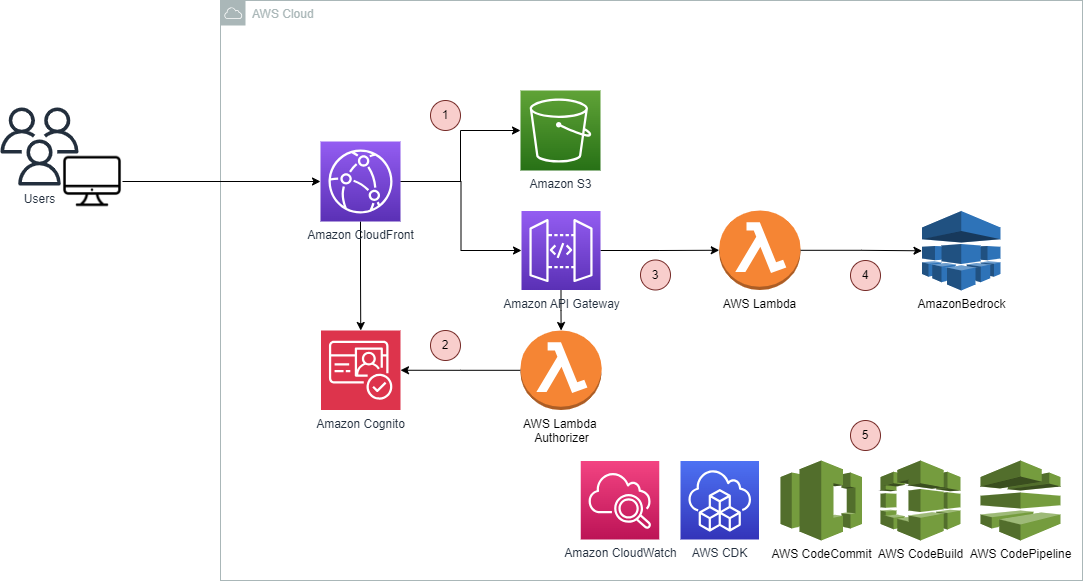
If we look at the architecture of this demo, you’ll see that nothing completely new is running behind the scenes. We keep it simple and elegant. Let’s have a deeper look at it:
- The frontend is a React Single Page Application (SPA) served to users on Amazon CloudFront and Amazon S3. CloudFront helps to distribute content to users quickly using AWS’s edge locations.
- The backend is hosted on Amazon API Gateway and AWS Lambda. The Lambda function takes user input and the chosen diagnostics from the web application (via API Gateway) and makes an API request to AWS Bedrock to generate a response.
- Amazon Cognito is used for authentication and authorization. It provides a customizable login/signup page and the ability to authorize calls to Bedrock via the Lambda function.
- Amazon Bedrock hosts Anthropic’s Claude, the foundation model used in the application.
We also wanted to make this solution’s infrastructure reusable and automate application builds and deployments. For this we used:
- AWS CDK (Cloud Development Kit) allows developers to define cloud application resources (e.g. AWS Services, IAM Policies, S3 buckets, lambda functions, etc.) using popular programming languages. AWS CDK simplifies infrastructure provisioning by allowing developers to write code to define and create cloud resources. All the services seen on the architecture diagram below are provisioned using AWS CDK.
- To automate the release of new application versions:
- Application code is stored in AWS CodeCommit.
- AWS CodeBuild compiles source code, runs tests, and produces ready-to-deploy software packages.
- AWS CodePipeline is used for automating the steps to build, test, and deploy the application.
- Amazon Cloudwatch provides us the ability to monitor our Lambda function and also other services used.
The overall system architecture can be found below.
Prompt Engineering
To get the best results from the Claude foundation model, we added instructions to the prompt, along with the diagnostic and user input. The instructions helped us to guide the Claude Model on its objective, limits, style, and tone when generating the response for a given user input. They also provided context for the conversation, which is the history of the discussion.
An important part of the prompt is its size limit. Models have different limits on the number of input and output tokens they can handle. For example, the Claude v4 model has an input token limit of 100,000 and can generate texts up to 60,000 words in length. This limit is much higher than the 8,192 token limit of ChatGPT.
To get good responses from the model, it is important to iterate and refine the prompt template.
Below you can find the prompt template used in the demo.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Human: You are a helpful medical AI assistant, competent to answer any medical related questions to non medical users. Use the following pieces of medical context, that you can summarize, to answer the question at the end.
But important points :
- If you don't know the answer, just say you don't know. Do NOT try to make up an answer.
- If the question is not related to the context, politely respond that you are tuned to only answer questions that are related to the context.
- If the question includes any greeting or polite word, respond accordingly.
- Before answering, analyze the question to determine the language used.
- Respond in the same language that the question is asked in.
- If you don't understand the question, respond by apologizing and asking for the question to be rephrased.
Context: (example medical diagnostic)
---------
This chest X-ray shows a large volume of free subdiaphragmatic gas. Given the history and examination, it is most likely secondary to perforation, possibly of a peptic ulcer from use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The patient should be made nil by mouth, given adequate analgesia and fluid resuscitated as necessary. An urgent referral to the general surgeons is required. A contrast enhanced CT of the abdomen and pelvis could be considered to identify the site of the perforation.
---------
Question: Could you please summarize the diagnostic? (example user input)
Assistant:
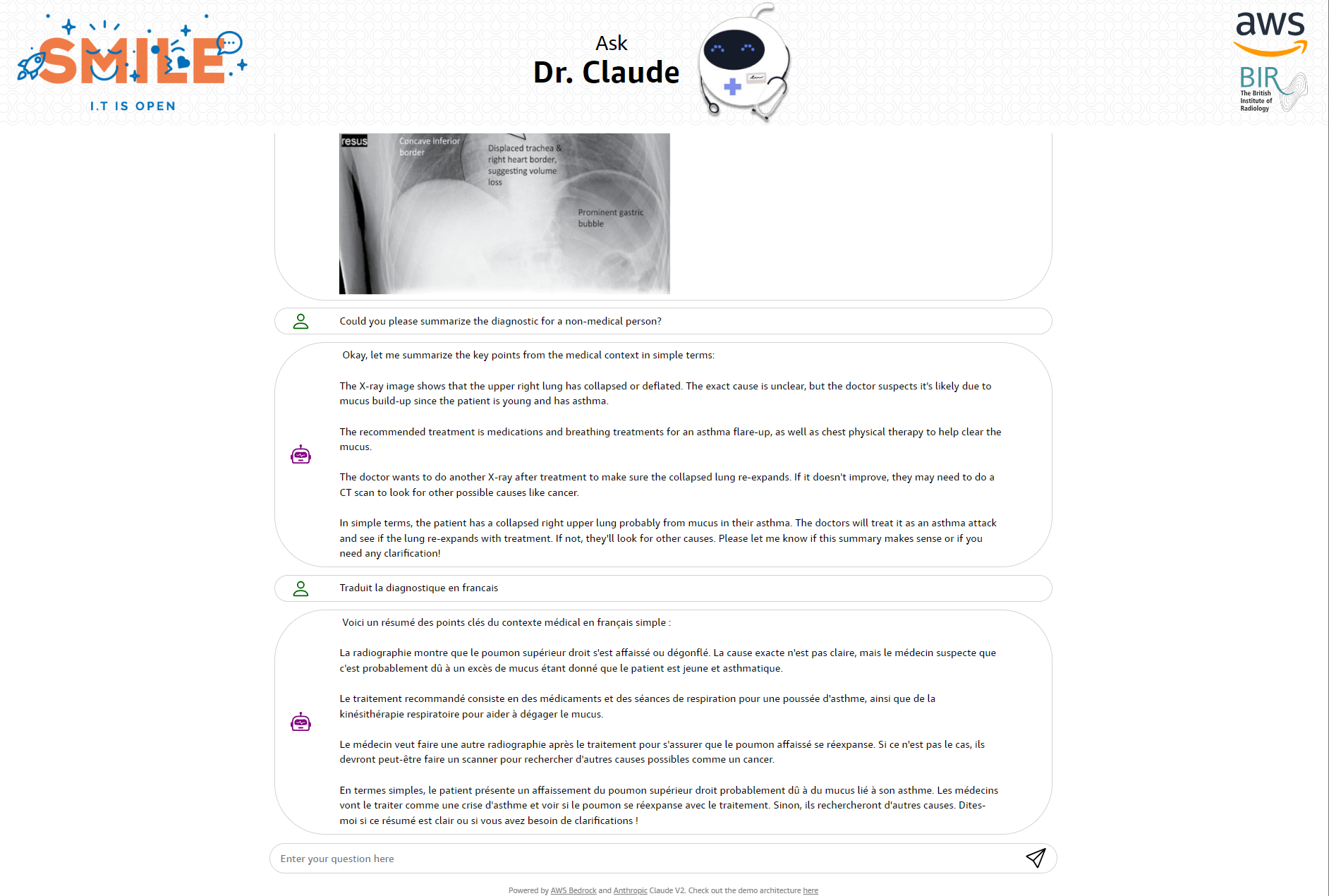
Screenshots
You can find below a couple of screenshots taken of the application, showcasing the usage, the types of questions asked, and the answers generated by the Claude model.

We also recorded a video of the demo :
How it went
As someone without a lot of AI/ML experience, I was able to develop a generative AI application in 10 days using AWS Bedrock. Bedrock makes it easy to train, test, deploy, scale, and maintain foundation models, which saves a lot of time and effort. Without Bedrock, I would have needed to work with a team of data scientists or spend a lot of time finding an open source model and hosting it myself.
AWS Bedrock is still under development, but it has a lot of potential. AWS is investing heavily in Anthropic, the company that developed Claude v2, the foundation model we used to build my application. We are excited to see what new features and capabilities AWS Bedrock will bring in the future.
At Smile, we are also interested in exploring ways to improve the quality of my application’s text generation by using a RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) source. RAG is a technique that uses a large language model (LLM) in conjunction with a retrieval model to access and incorporate external knowledge. This external knowledge is typically a vector database that stores documents in the form of embeddings. We may write a future series of blog posts about how to deploy different RAG sources on AWS. Stay tuned!
Sources
